Vehicle mechatronics
Topics on the field of vehicle mechatronics
Component level design
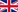
- modeling
- qualitative specifications (trajectory following, driving stability, comfort, fuel, exhaust emissions),
- robust control methods and algorithms
Cooperative control
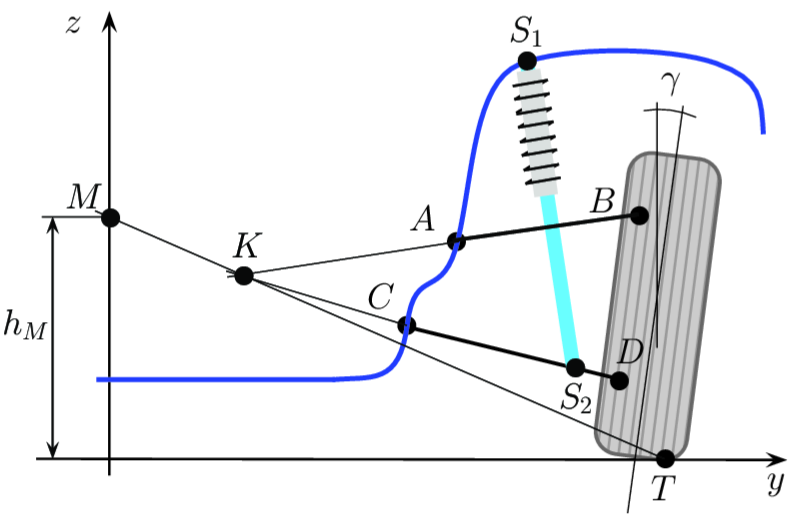
Ensure the cooperation of the vehicles with the goals of (reducing fuel consumption and emissions).
Effects of the V2I/V2V communication:
- Transport (average speed, vehicle density, waiting time)
- Driving assistance (parking and lane/object detection)
- Safety (detecting potentially dangerous situations, safety/hazards of changing lanes, warning of rapid deceleration/stop)
Intergated control design
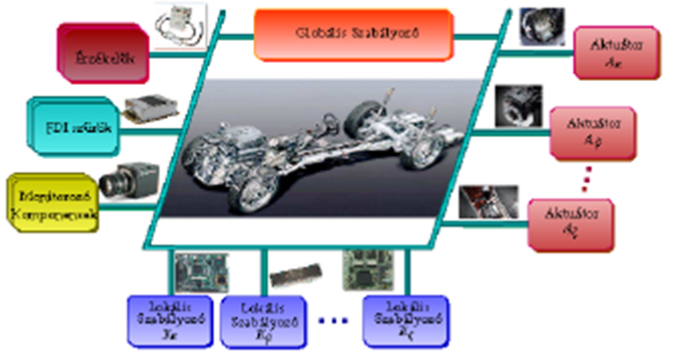
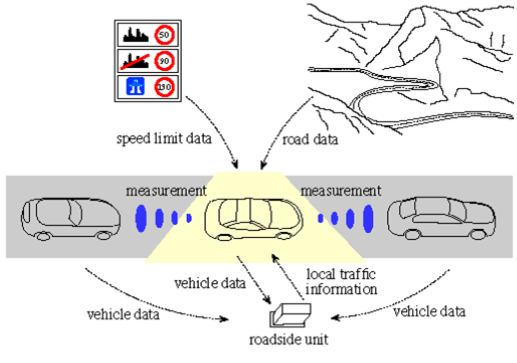
Coordinated control of the influencing dynamic active actuators to prescribe operational requirements, in order to guarantee and increase safety and reliability.
- Priority: ensuring the hierarchy between the actuators
- Reconfigurable: guarantee of the changed quality tasks
- Fault-tolerance control: manages the possible failure of the component
Coordinating the control system of the vehicle with the driver and the infrastructure

Factors of the Multi-criteria design task
- travelling and shipping
- energy demand, consumption
- topography
- restrictive boards, prescript
- transporting vehicles
- exhaust emissions
- driver demands
Communication
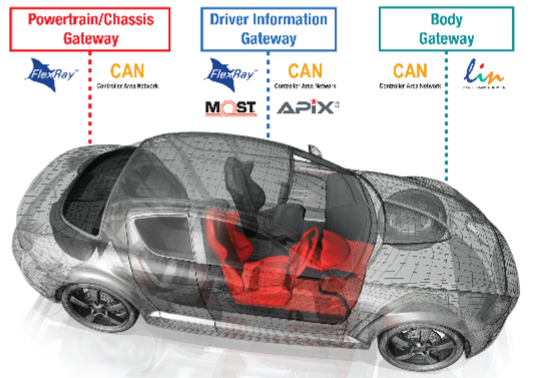
Collecting vehicle state information, this information is safely used for developing new functions
Vehicle networks
- CAN, LIN, FlexRay
- Wireless data transfer
V2V and V2I communication
- ad-hoc networks between vehicles
Cloud computing
- Vehicle gateways
- Smartphone platforms
- Vehicle fleet management
Embedded systems

Developing future functions, requirements, and architecture of automotive electronic control units.
- Automotive microcontroller architectures
- Hardware design
- Software design
- Environmental resistance testing, automotive quality assurance standards
- Sensorfusion
- Autonomous functions
- Software-in-the-Loop (SIL) and Hardware-in-the-Loop (HIL) testing and simulations.